A fancy color diamond is a natural diamond that exhibits a distinct and attractive hue, which makes it a rarity in the world of diamonds. Unlike colorless diamonds, which are graded on a D-Z scale, fancy color diamonds are graded on a separate scale that considers their color intensity, hue, and saturation. These diamonds are found in a variety of colors, such as red, blue, green, yellow, orange, pink, purple, gray, and brown. Below is an in-depth look at each color:
Red Diamonds:
Red diamonds are the rarest and most valuable of all fancy color diamonds. They are often found with secondary hues, such as brownish-red or purplish-red. The color in red diamonds is believed to be caused by the presence of nitrogen and changes in the diamond's crystal lattice structure.
Blue Diamonds:
Blue diamonds are extremely rare and highly sought after. Their color is attributed to the presence of boron impurities in the diamond's crystal lattice. The most famous blue diamond is the Hope Diamond, a 45.52-carat gem with a deep blue color.
Green Diamonds:
Green diamonds are rare and can exhibit a range of green hues, from light to dark. Their color is a result of natural irradiation, which occurs when the diamond is exposed to radiation during its formation in the Earth's mantle. The most famous green diamond is the 41-carat Dresden Green Diamond.
Yellow Diamonds:
Yellow diamonds, also known as canary diamonds, are more common than other fancy color diamonds. Their color is caused by the presence of nitrogen atoms in the crystal lattice. The intensity of the yellow color can range from light to deep, with vivid yellow diamonds being the most valuable.
Orange Diamonds:
Orange diamonds are quite rare and derive their color from the presence of nitrogen in the crystal lattice. The color can range from light to deep orange, with pure, vivid orange diamonds being the most valuable.
Pink Diamonds:
Pink diamonds are rare and highly sought after, particularly those with a pure pink hue. The cause of their color is still debated, but it is believed to be due to changes in the diamond's crystal lattice structure caused by intense pressure during formation.
Purple Diamonds:
Purple diamonds are incredibly rare, with their color resulting from hydrogen-related defects in the crystal lattice. They can exhibit a range of purple hues, from light lavender to deep violet.
Gray Diamonds:
Gray diamonds are less common and are caused by the presence of hydrogen or boron impurities in the crystal lattice. The color can range from light to dark gray, with even-toned gray diamonds being the most valuable.
Brown Diamonds:
Brown diamonds, also known as chocolate or cognac diamonds, are relatively common compared to other fancy color diamonds. The color is caused by plastic deformation of the crystal lattice during the diamond's formation.
-
DIAMOND⠀⠀
New -
SHOP BY CATEGORY
-
SHOP BY SHAPE
-
SHOP BY COLOR
-
PERFECT FOR YOU!
-
-
JEWELRY⠀⠀
-
SHOP BY CATEGORY
-
SHOP BY STONE
-
DESIGN YOUR OWN
-
SPECIAL ONE!
Slice Rose Cut Diamond Pendant, Salt And Pepper Diamond, Yellow Gold Pendant, Bridal NecklaceRegular price $1,800.00
-
-
RINGS⠀⠀
-
SHOP BY RING STYLE
-
ENGAGEMENT RINGS
-
WEDDING RING
-
FEATURED RING!
Round Diamond Salt And Pepper Diamond Natural Diamond Ring Gold Ring Engagement RingRegular price $500.00
-
-
EDUCATION⠀⠀
-
FAQs⠀⠀
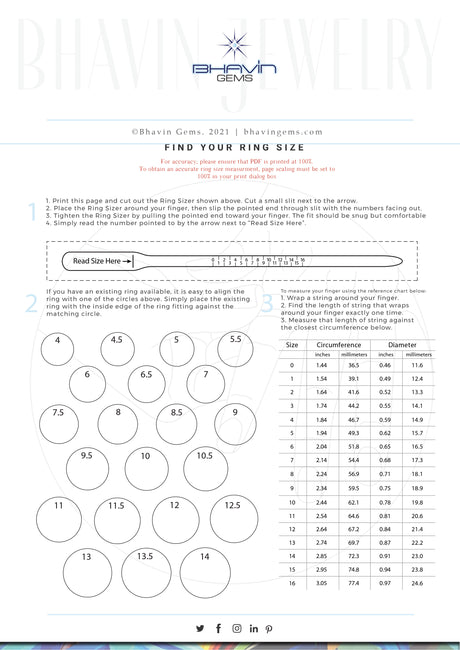
Bhavin Ring Sizer

This is a chart that will be extremely helpful for you to determine the ring size that you need. You can either make use of a tape or a small piece of string to measure the area that will be occupied by the ring. When it becomes a complete circle, make a mark on such string. This will be helpful for you to compare with the chart that is mentioned below.
1: Print out the Ring Size guide and cut out the sizing tool. Slide the end tab of sizing tool through slot Ring Size Here vertical line and wrap the sizer around the base of the finger. Make sure to allow size for the knuckle. The number aligned with slot line is your ring size
2:Place a ring that fits intended finger you are shopping for on each circle until you find one that matches. The black circle should trace the inside of your ring.
3:To measure your finger using the reference chart: 1. Wrap a string around your finger. 2. Find the length of string that wraps around your finger exactly one time. 3. Measure that length of string against the closest circumference in chart.